R Programming Training by Experts
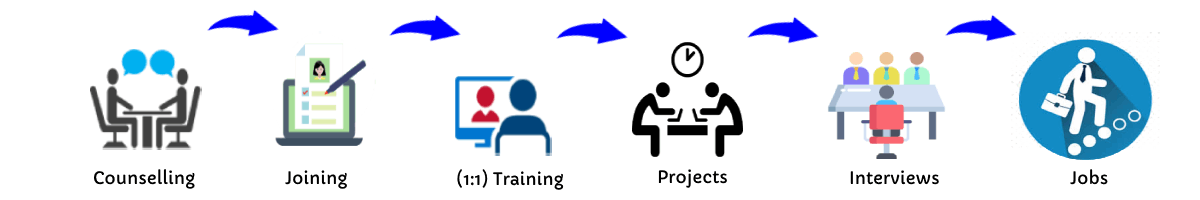
Our Training Process
R Programming - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
THE ART OF R PROGRAMMING
- Why Use R for Your Statistical Work?
- Object-Oriented Programming
- Functional Programming?
- Functional Programming?
- Downloading R from CRAN
- Installing from Source
- Interactive Mode
- Batch Mode
- Variable Scope
- Default Arguments
- Vectors, the R
- Character Strings
- Matrices
- Lists
- Arrays
- Data Frames
- Adding and Deleting Vector Elements
- Obtaining the Length of a Vector
- Matrices and Arrays as Vectors
- Vector Arithmetic and Logical Operations
- Vector Indexing
- Generating Useful Vectors with the : Operator
- Generating Vector Sequences with seq()
- Repeating Vector Constants with rep
- Vector In, Vector Out
- Vector In, Matrix Out
- Using NA
- Using NULL
- Generating Filtering Indices
- Filtering with the subset() Function
- The Selection Function which
- Extended Example: A Measure of Association
- Extended Example: Recoding an Abalone Data Set
- General Matrix Operations
- Performing Linear Algebra Operations on Matrices
- Matrix Indexing
- Filtering on Matrices
- Using the apply() Function
- Extended Example: Finding Outliers
- Adding and Deleting Matrix Rows and Columns
- Changing the Size of a Matrix
- List Indexing
- Adding and Deleting List Elements
- Getting the Size of a List
- Using the lapply() and sapply() Functions
- Naming Columns and Rows
- Accessing Array Elements
- Check if an Item Exists
- Amount of Rows and Columns
- Array Length
- Manipulating Array Elements
- Calculations Across Array Elements
- Accessing Data Frames
- Extracting Subdata Frames
- More on Treatment of NA Values
- Using the rbind() and cbind() Functions and Alternatives .
- Applying apply()
- Extended Example: An Employee Database
- Using lapply() and sapply() on Data Frames
- The tapply() Function
- The split() Function
- The by() Function
- Matrix/Array-Like Operations on Tables
- Extended Example: Extracting a
- The aggregate() Function
- The cut() Function
- Loops
- Looping Over Non vector Sets if-else
- Deciding Whether to Explicitly Call return()
- Returning Complex Objects
- The Scope Hierarchy
- More on ls()
- Functions Have (Almost) No Side Effects
- Writing to Nonlocals with the Super assignment Operator
- Writing to Nonlocals with assign()
- What’s Considered a Replacement Function?
- Text Editors and Integrated Development Environments
- Extended Example
- Cumulative Sums and Products
- Minima and Maxima
- Extended Example: Vector Cross Product
- Set Operations
- Built-In Random Variate Generators
- Obtaining the Same Random Stream in Repeated Runs
- Using the scan() Function
- Using the readline() Function
- Printing to the Screen
- Reading a Data Frame or Matrix from a File
- Reading Text Files
- Introduction to Connections
- Extended Example
- Accessing Files on Remote Machines via URLs
- Writing to a File
- Getting File and Directory Information
- grep()
- nchar()
- paste()
- sprintf()
- substr
- strsplit()
- regexpr()
- Extended Example
- Reading a CSV File
- Analyzing the CSV File
- Writing into a CSV File
- Install xlsx Package
- Reading the Excel File
- Writing the Binary File
- Reading the Binary File
- Reading XML File
- XML to Data Frame
- Install rjson Package
- Read the JSON File
- Convert JSON to a Data Frame
- RMySQL Package
- Connecting R to MySql
- Querying the Tables
- Query with Filter Clause
- Updating Rows in the Tables
- Inserting Data into the Tables
- Creating Tables in MySql
- Dropping Tables in MySql
- The Workhorse of R Base Graphics: The plot() Function
- R - Pie Charts
- R - Bar Charts
- R - Boxplots
- R - Histograms
- R - Line Graphs
- R - Scatterplots
- Starting a New Graph While Keeping the Old Ones
- Extended Example
- Adding Points: The points() Function
- Adding a Legend: The legend() Function
- Adding Text: The text() Function
- Pinpointing Locations: The locator() Function
- Restoring a Plot
- Customizing Graphs
- Changing Character Sizes: The cex
- Changing the Range of Axes: The xlim and ylim Options
- Graphing Explicit Functions
- Extended Example
- R Graphics Devices
- Saving the Displayed Graph
- Closing an R Graphics Device
INTRODUCTION
INSTALLING R
GETTING STARTED
How to Run R
First R Session
Introduction to Functions
Preview of Some Important R Data Structures
VECTORS
Scalars, Vectors, Arrays, and Matrices
Declarations
Common Vector Operations
Vectorized Operations
NA and NULL Values
Filtering
A Vectorized if-then-else: The ifelse() Function
Testing Vector Equality
Vector Element Names
More on c()
MATRICES AND ARRAYS
Creating Matrices
Applying Functions to Matrix Rows and Columns
More on the Vector/Matrix Distinction
Avoiding Unintended Dimension Reduction
Naming Matrix Rows and Columns
Higher-Dimensional Arrays
LISTS
Creating Lists
General List Operations
Accessing List Components and Values
Applying Functions to Lists
ARRAYS
DATA FRAMES
Creating Data Frames
Other Matrix-Like Operations
Merging Data Frames
Applying Functions to Data Frames
FACTORS AND TABLES
Factors and Levels
Common Functions Used with Factors
Working with Tables
Other Factor- and Table-Related Functions
R PROGRAMMING STRUCTURES
Control Statements
Arithmetic and Boolean Operators and Values
Default Values for Arguments
Return Values
Functions Are Objects
Environment and Scope Issues
The Top-Level Environment
No Pointers in R
Writing Upstairs
When Should You Use Global Variables?
Replacement Functions
Tools for Composing Function Code
The edit() Function
Writing Your Own Binary Operations
Anonymous Functions
DOING MATH AND SIMULATIONS IN R
Math Functions
Functions for Statistical Distributions
Sorting
Linear Algebra Operations on Vectors and Matrices
Simulation Programming in R
INPUT/OUTPUT
Accessing the Keyboard and Monitor
Reading and Writing Files
STRING MANIPULATION
An Overview of String-Manipulation Functions
Regular Expressions
R DATA INTERFACES
R - CSV Files
R - Excel Files
R - Binary Files
R - XML Files
R - JSON Files
R - Database
GRAPHICS
Creating Graphs
Saving Graphs to Files
Creating Three-Dimensional Plots
R Statistics
R Statistics Intro
R Data Set
R Max and Min
R Mean Median Mode
R Percentiles
INSTALLING AND USING PACKAGES
Package Basics
Loading a Package from Your Hard Drive
Downloading a Package from the Web
Installing Packages Automatically
Installing Packages Manually
Listing the Functions in a Package
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 Many large companies, including prominent banks, IT, retail, healthcare, pharmaceutical, supply chain, and logistics industries, adopt R. You'll learn how to build and setup software for a statistical programming environment, as well as how to represent generic programming language concepts in a high-level statistical language. In R, there are a variety of great packages that can aid in a fast data analysis. Nestsoft is the excellent R programming Training in kerala . Because of its open source credibility, R programming is quickly becoming most in expert in the field of analytics. With the help of R programming, massive datasets may be analysed in less time. The course provides students hands-on experience with a variety of R programming principles. While teaching R Programming in the classroom, our Nestsoft trainers discuss their previous and current project experiences with candidates, allowing them to gain exposure to real-world business experience. R is a computer language that can be used for statistical analysis, reporting, and graphics. There is a significant shortage of experts with R programming skills on the market, which brings attention to pursue.
Many large companies, including prominent banks, IT, retail, healthcare, pharmaceutical, supply chain, and logistics industries, adopt R. You'll learn how to build and setup software for a statistical programming environment, as well as how to represent generic programming language concepts in a high-level statistical language. In R, there are a variety of great packages that can aid in a fast data analysis. Nestsoft is the excellent R programming Training in kerala . Because of its open source credibility, R programming is quickly becoming most in expert in the field of analytics. With the help of R programming, massive datasets may be analysed in less time. The course provides students hands-on experience with a variety of R programming principles. While teaching R Programming in the classroom, our Nestsoft trainers discuss their previous and current project experiences with candidates, allowing them to gain exposure to real-world business experience. R is a computer language that can be used for statistical analysis, reporting, and graphics. There is a significant shortage of experts with R programming skills on the market, which brings attention to pursue.